Posts Tagged Philosophy of Science
Popular Miscarriages of Science, part 3 – The Great Lobotomy Rush
Posted by Bill Storage in History of Science on January 25, 2024
On Dec. 16, 1960, Dr. Walter Freeman told his 12-year-old patient Howard Dully that he was going to run some tests. Freeman then delivered four electric shocks to Dully to put him out, writing in his surgery notes that three would have been sufficient. Then Freeman inserted a tool resembling an ice pick above Dully’s eye socket and drove it several inches into his brain. Dully’s mother had died five years earlier. His stepmother told Freeman, a psychiatrist, that Dully had attacked his brother, something the rest of Dully’s family later said never happened. It was enough for Freeman to diagnose Dully as schizophrenic and perform another of the thousands of lobotomies he did between 1936 and 1967.
“By some miracle it didn’t turn me into a zombie,” said Dully in 2005, after a two-year quest for the historical details of his lobotomy. His story got wide media coverage, including an NPR story called My Lobotomy’: Howard Dully’s Journey. Much of the media coverage of Dully and lobotomies focused on Walter Freeman, painting Freeman as a reckless and egotistical monster.
Weston State Hospital (Trans-Allegheny Lunatic Asylum), photo courtesy of Tim Kiser
In The Lobotomy Letters: The Making of American Psychosurgery, (2015) Mical Raz asks, “Why, during its heyday was there nearly no objection to lobotomy in the American medical community?” Raz doesn’t seem to have found a satisfactory answer.
(I’m including a lot of in-line references here, not to be academic, but because modern media coverage often disagrees with primary sources and scholarly papers on the dates, facts, and numbers of lobotomy. It appears that most popular media coverage seemed to use other current articles as their sources, rather than going to primary sources. As a trivial example, Freeman’s notes report that in Weston, WV, he did 225 lobotomies in 12 days. The number 228 is repeated in all the press on Howard Dully. This post is on the longer side, because the deeper I dug, the less satisfied I became that we have learned the right lesson from lobotomies.)
A gripping account of lobotomies appeared in Dr. Paul Offit’s (developer of the rotavirus vaccine) 2017 Pandora’s Lab. It tells of a reckless Freeman buoyed by unbridled media praise. Offit’s piece concludes with a warning about wanting quick fixes. If it seems too good to be true, it probably is.
In the 2005 book, The Lobotomist: A Maverick Medical Genius and his Tragic Quest to Rid the World of Mental Illness, Jack El-Hai gave a much more nuanced account, detailing many patients who thought their lobotomies hade greatly improved their lives. El-Hai’s Walter Freeman was on a compassionate crusade to help millions of asylum patients escape permanent incarceration in gloomy state mental institutions. El-Hai documents Freeman’s life-long postoperative commitment to his patients, crisscrossing America to visit the patients that he had crisscrossed America to operate on. Despite performing most of his surgery in state mental hospitals, Freeman always refused to operate on people in prison, against pressure from defense attorneys’ pleas to render convicts safe for release.
Contrasting El-Hai’s relatively kind assessment, the media coverage of Dully aligns well with Offit’s account in Pandora’s Lab. On researching lobotomies, opinions of the medical community, and media coverage, I found I disagreed with Offit’s characterization of the media coverage, more about which below. In all these books I saw signs that lobotomies are a perfect instance of bad science in the sense of what Thomas Kuhn and related thinkers would call bad science, so I want to dig into that here. I first need to expand on Kuhn, his predecessors, and his followers a bit.
Kuhn’s Precursors and the Kuhnian Groupies
Kuhn’s writing, particularly Structure of Scientific Revolutions, was unfortunately ambiguous. His friends, several of whom I was lucky enough to meet, and his responses to his critics tell us that he was no enemy of science. He thought science was epistemically special. But he thought science’s claims to objectivity couldn’t be justified. Science, in Kuhn’s view, was not simply logic applied to facts. In Structure, Kuhn wrote many things that had been said before, though by sources Kuhn wasn’t aware of.
Karl Marx believed that consciousness was determined by social factors and that thinking will always be ideological. Marx denied that what Francis Bacon (1561-1626) had advocated was possible. I.e., we can never intentionally free our minds of the idols of the mind, the prejudices resulting from social interactions and from our tribe. Kuhn partly agreed but thought that communities of scientists engaged in competitive peer review could still do good science.
Ludwik Fleck’s 1935 Genesis and Development of a Scientific Fact argued that science was a thought collective of a community whose members share values. In 1958, Norwood Hanson, in Patterns of Discovery, wrote that all observation is theory-laden. Hanson agreed with Marx that neutral observation cannot exist, so neither can objective knowledge. “Seeing is an experience. People see, not their eyes,” said Hanson.
Most like Kuhn was Michael Polanyi, a brilliant Polish polymath (chemist, historian, economist). In his 1946 Science, Faith and Society, Polanyi wrote that scientific knowledge was produced by individuals under the influence of the scientific collectives in which they operated. Polanyi long preceded Kuhn, who was unaware of Polanyi’s work, in most of Kuhn’s key concepts. Unfortunately, Polanyi’s work didn’t appear in English until after Kuhn was famous. An aspect of Polanyi’s program important to this look at lobotomies is his idea that competition in science works like competition in business. The “market” determines winners of competing theories based on the judgments of its informed participants. Something like a market process exists within the institutional structure of scientific research.
Kuhn’s Structure was perfectly timed to correspond to the hippie/protest era, which distrusted big pharma and the rest of science, and especially the cozy relationships between academia, government, and corporations – institutions of social and political power. Kuhn had no idea that he was writing what would become one of the most influential books of the century, and one that became the basis for radical anti-science perspectives. Some communities outright declared war on objectivity and rationality. Science was socially constructed, said these “Kuhnians.” Kuhn was appalled.
A Kuhnian Take on Lobotomies
Folk with STEM backgrounds might agree that politics and influence can affect which scientific studies get funded but would probably disagree with Marx, Fleck, and Hanson that interest, influence, and values permeate scientific observations (what evidence gets seen and how it is assimilated), the interpretation of measurements and data, what data gets dismissed as erroneous or suppressed, and finally the conclusions drawn from observations and data.
The concept of social construction is in my view mostly garbage. If everything is socially constructed, then it isn’t useful to say of any particular thing that it is socially constructed. But the Kuhnians, who, oddly, have now come to trust institutions like big pharma, government science, and Wikipedia, were right in principle that science is in some legitimate sense socially constructed, though they were perhaps wrong about the most egregious cases, then and now. The lobotomy boom seems a good fit for what the Kuhnians worried about.
If there is going to be a public and democratic body of scientific knowledge (science definition 2 above) based on scientific methods and testability (definition 1 above), some community of scientists has to agree on what has been tested and falsified for the body of knowledge to get codified and publicized. Fleck and Hanson’s positions apply here. To some degree, that forces definition 3 onto definitions 1 and 2. For science to advance mankind, the institution must be cognitively diverse, it must welcome debate and court refutation, and it must be transparent. The institutions surrounding lobotomies did none of these. Monstrous as Freeman may have been, he was not the main problem – at least not the main scientific problem – with lobotomies. This was bad institutional science, and to the extent that we have missed what was bad about it, it is ongoing bad science. There is much here to make your skin crawl that was missed by NPR, Offit’s Pandora’s Lab, and El-Hai’s The Lobotomist.
Background on Lobotomy
In 1935 António Egas Moniz (1874–1955) first used absolute alcohol to destroy the frontal lobes of a patient. The Nobel Committee called it one of the most important discoveries ever made in psychiatric medicine, and Moniz became a Nobel laureate in 1949. In two years Moniz oversaw about 40 lobotomies. He failed to report cases of vomiting, diarrhea, incontinence, hunger, kleptomania, disorientation, and confusion about time in postoperative patients who lacked these conditions before surgery. When the surgery didn’t help the schizophrenia or whatever condition it was done to cure, Moniz said the patients’ conditions had been too advanced before the surgery.
In 1936 neurologist Walter Freeman, having seen Moniz’s work, ordered the first American lobotomy. James Watts of George Washington University Hospital performed the surgery by drilling holes in the side of the skull and removing a bit of brain. Before surgery, Freeman lied to the patient, who was concerned that her head would be shaved, about the procedure. She didn’t consent, but her husband did. The operation was done anyway, and Freeman declared success. He was on the path to stardom.
The patient, Alice Hammatt, reported being happy as she recovered. A week after the operation, she developed trouble communicating, was disoriented, and experienced anxiety, the condition the lobotomy was intended to cure. Freeman presented the case at a medical association meeting, calling the patient cured. In that meeting, Freeman was surprised to find that he faced criticism. He contacted the local press and offered an exclusive interview. He believed that the press coverage would give him a better reception at his next professional lobotomy presentation.
By 1952, 18,000 lobotomies had been performed in the US, 3000 of which Freeman claimed to have done. He began doing them himself, despite having no training in surgery, after Watts cut ties because of Freeman’s lack of professionalism and sterilization. Technically, Freeman was allowed to perform the kind of lobotomies he had switched to, because it didn’t involve cutting. Freeman’s new technique involved using a tool resembling an ice pick. Most reports say it was a surgical orbitoclast, though Freeman’s son Frank reported in 2005 that his father’s tool came right out their kitchen cabinet. Freeman punched a hole through the eye sockets into the patient’s frontal lobes. He didn’t wear gloves or a mask. West Virginians received a disproportionate share of lobotomies. At the state hospital in Weston, Freeman reports 225 lobotomies in twelve days, averaging six minutes per procedure. In The Last Resort: Psychosurgery and the Limits of Medicine (1999), JD Pressman reports a 14% mortality rate in Freeman’s operations.
The Press at Fault?
The press is at the center of most modern coverage of lobotomies. In Pandora’s Lab, Offit, as in other recent coverage, implies that the press overwhelmingly praised the procedure from day one. Offit reports that a front page article in the June 7, 1937 New York Times “declared – ‘in what read like a patent medicine advertisement – that lobotomies could relieve ‘tension apprehension, anxiety, depression, insomnia, suicidal ideas, …’ and that the operation ‘transforms wild animals into gentle creatures in the course of a few hours.’”
I read the 1937 Times piece as far less supportive. In the above nested quote, The Times was really just reporting the claims of the lobotomists. The headline of the piece shows no such blind faith: “Surgery Used on the Soul-Sick; Relief of Obsessions Is Reported.” The article’s subhead reveals significant clinical criticism: “Surgery Used on the Soul-Sick Relief of Obsessions Is Reported; New Brain Technique Is Said to Have Aided 65% of the Mentally Ill Persons on Whom It Was Tried as Last Resort, but Some Leading Neurologists Are Highly Skeptical of It.”
The opening paragraph is equally restrained: “A new surgical technique, known as “psycho-surgery,” which, it is claimed, cuts away sick parts of the human personality, and transforms wild animals into gentle creatures in the course of a few hours, will be demonstrated here tomorrow at the Comprehensive Scientific Exhibit of the American Medical Association…“
Offit characterizes medical professionals as being generally against the practice and the press as being overwhelmingly in support, a portrayal echoed in NPR’s 2005 coverage. I don’t find this to be the case. By Freeman’s records, most of his lobotomies were performed in hospitals. Surely the administrators and staff of those hospitals were medical professionals, so they couldn’t all be against the procedure. In many cases, parents, husbands, and doctors ordered lobotomies without consent of the patient, in the case of institutionalized minors, sometimes without consent of the parents. The New England Journal of Medicine approved of lobotomy, but an editorial in the 1941 Journal of American Medical Association listed the concerns of five distinguished critics. As discussed below, two sub-communities of clinicians may have held opposing views, and the enthusiasm of the press has been overstated.
In a 2022 paper, Lessons to be learnt from the history of lobotomy, Oivind Torkildsen of the Department of Clinical Medicine at University of Bergen wrote that “the proliferation of the treatment largely appears to have been based on Freeman’s charisma and his ability to enthuse the public and the news media.” Given that lobotomies were mostly done in hospitals staffed by professionals ostensibly schooled in and practicing the methods of science, this seems a preposterous claim. Clinicians would not be swayed by tabloids.
A 1999 article by GJ Diefenbach in the Journal of the History of the Neurosciences, Portrayal of Lobotomy in the Popular Press: 1935-1960, found that the press initially used uncritical, sensational reporting styles, but became increasingly negative in later years. The article also notes that lobotomies faced considerable opposition in the medical community. It concluded that popular press may have been a factor influencing the quick and widespread adoption of lobotomy.
The article’s approach was to randomly distribute articles to two evaluators for quantitative review. The reviewers then rated the tone of the article on a five-point scale. I plotted its data, and a linear regression (yellow line below) indeed shows that the non-clinical press cooled on lobotomies from 1936 to 1958 (though, as is apparent from the broad data scatter, linear regression doesn’t tell the whole story). But the records, spotty as they are, of when the bulk of lobotomies were performed should also be considered. Of the 20,000 US lobotomies, 18,000 of them were done in the 5-year period from 1948 to 1952, the year that phenothiazines entered psychiatric clinical trials. A linear regression of the reviewers’ judgements over that period (green line) shows little change.
Applying the Methods of History and Philosophy of Science
One possibility for making sense of media coverage in the time, the occurrence of lobotomies, and the current perception of why lobotomies persisted despite opposition in the medical community is to distinguish between lobotomies done in state hospitals from those done in private hospitals or psychiatrists’ offices. The latter category dominated the press in the 1940s and modern media coverage. The tragic case of Rosemary Kennedy, whose lobotomy left her institutionalized and abandoned by her family and that of Howard Dully are far better known that the 18,000 lobotomies done in American asylums. Americans were not as in love with lobotomies as modern press reports. The latter category, private hospital lobotomies, while including some high-profile cases, was small compared to the former.
Between 1936 and 1947, only about 1000 lobotomies had been performed in the US, despite Howard Freeman’s charisma and self-promotion. We, along with Offit and NPR, are far too eager to assign blame to Howard Freeman the monster than to consider that the relevant medical communities and institutions may have been monstrous by failing to critically review their results during the lobotomy boom years.
This argument requires me to reconcile the opposition to lobotomies appearing in medical journals from 1936 on with the blame I’m assigning to that medical community. I’ll start by noting that while clinical papers on lobotomy were plentiful (about 2000 between 1936 and 1952), the number of such papers that addressed professional ethics or moral principles was shockingly small. Jan Frank, in Some Aspects of Lobotomy (Prefrontal Leucotomy) under Psychoanalytic Scrutiny (Psychiatry 13:1, 1950) reports a “conspicuous dearth of contributions to the theme.” Constance Holden, in Psychosurgery: Legitimate Therapy or Laundered Lobotomy? (Science, Mar. 16, 1973), concluded that by 1943, medical consensus was against lobotomy, and that is consistent with my reading of the evidence.
Enter Polanyi and the Kuhnians
In 2005, Dr. Elliot Valenstein (1923-2023), 1976 author of Great and Desperate Cures: The Rise and Decline of Psychosurgery, in commenting on the Dully story, stated flatly that “people didn’t write critical articles.” Referring back to Michael Polanyi’s thesis, the medical community failed itself and the world by doing bad science – in the sense that suppression of opposing voices, whether through fear of ostracization or from fear of retribution in the relevant press, destroyed the “market’s” ability to get to the truth.
By 1948, the popular lobotomy craze had waned, as is shown in Diefenbach’s data above, but the institutional lobotomy boom had just begun. It was tucked away in state mental hospitals, particularly in California, West Virginia, Virginia, Washington, Ohio, and New Jersey.
Jack Pressman, in Last resort: Psychosurgery and the Limits of Medicine (1998), seems to hit the nail on the head when he writes “the kinds of evaluations made as to whether psychosurgery worked would be very different in the institutional context than it was in the private practice context.”
Doctors in asylums and mental hospitals lived in a wholly different paradigm from those in for-profit medicine. Funding in asylums was based on patient count rather than medical outcome. Asylums were allowed to perform lobotomies without the consent of patients or their guardians, to whom they could refuse visitation rights.
While asylum administrators usually held medical or scientific degrees, their roles as administrators in poorly funded facilities altered their processing of the evidence on lobotomies. Asylum administrators had a stronger incentive than private practices to use lobotomies because their definitions of successful outcome were different. As Freeman wrote in a 1957 follow-up of 3000 patients, lobotomized patients “become docile and are easier to manage”. Success in the asylum was not a healthier patient, it was a less expensive patient. The promise of a patient’s being able to return to life outside the asylum was a great incentive for administrators on tight budgets. If those administrators thought lobotomy was ineffective, they would have had no reason to use it, regardless of their ethics. The clinical press had already judged it ineffective, but asylum administrators’ understanding of effectiveness was different from that of clinicians in private practice.
Pressman cites the calculus of Dr. Mesrop Tarumianz, administrator of Delaware State Hospital: “In our hospital, there are 1,250 cases and of these about 180 could be operated on for $250 per case. That will constitute a sum of $45,000 for 180 patients. Of these, we will consider that 10 percent, or 18, will die, and a minimum of 50 percent of the remaining, or 81 patients will become well enough to go home or be discharged. The remaining 81 will be much better and more easily cared for the in hospital… That will mean a savings $351,000 in a period of ten years.”
The point here is not that these administrators were monsters without compassion for their patients. The point is that significant available evidence existed to conclude that lobotomies were somewhere between bad and terrible for patients, and that this evidence was not processed by asylum administrators in the same way it was in private medical practice.
The lobotomy boom was enabled by sensationalized headlines in the popular press, tests run without control groups, ridiculously small initial sample sizes, vague and speculative language by Moniz and Freeman, cherry-picked – if not outright false – trial results, and complacence in peer review. Peer review is meaningless unless it contains some element of competition.
Some might call lobotomies a case of conflict of interest. To an extent that label fits, not so much in the sense that anyone derived much personal benefit in their official capacity, but in that the aims and interests of the involved parties – patients and clinicians – were horribly misaligned.
The roles of asylum administrators – recall that they were clinicians too – did not cause them to make bad decisions about ethics. Their roles caused and allowed them to make bad decisions about lobotomy effectiveness, which was an ethics violation because it was bad science. Different situations in different communities – private and state practices – led intelligent men, interpreting the same evidence, to reach vastly different conclusions about pounding holes in people’s faces.
It will come as no surprise to my friends that I will once again invoke Paul Feyerabend: if science is to be understood as an institution, there must be separation of science and state.
___
Epilogical fallacies
A page on the official website the Nobel prize still defends the prize awarded to Moniz. It uncritically accepts Freeman’s statistical analysis of outcomes, e.g., 2% of patients became worse after the surgery.
…
Wikipedia reports that 60% of US lobotomy patients were women. Later in the same article it reports that 40% of US lobotomies were done on gay men. Thus, per Wikipedia, 100% of US male lobotomy patients were gay. Since 18,000 of the 20,000 lobotomies done in the US were in state mental institutions, we can conclude that mental institutions in 1949-1951 overwhelmingly housed gay men. Histories of mental institutions, even those most critical of the politics of deinstitutionalization, e.g. Deinstitutionalization: A Psychiatric Titanic, do not mention gay men.
…
Elliot Valenstein, cited above, wrote in a 1987 Orlando Sentinel editorial that all the major factors that shaped the lobotomy boom are still with us today: “desperate patients and their families still are willing to risk unproven therapies… Ambitious doctors can persuade some of the media to report untested cures with anecdotal ‘research’… it could happen again.” Now let’s ask ourselves, is anything equivalent going on today, any medical fad propelled by an uncritical media and single individual or small cadre of psychiatrists, anything that has been poorly researched and might lead to disastrous outcomes? Nah.
Extraordinary Miscarriages of Science, Part 2 – Creation Science
Posted by Bill Storage in History of Science on January 21, 2024
By Bill Storage, Jan. 21, 2024
Creation Science can refer either to young-earth or old-earth creation theories. Young Earth Creationism (YEC) makes specific claims about the creation of the universe from nothing, the age of the earth as inferred from the Book of Genesis and about the creation of separate “kinds” of creatures. Wikipedia’s terse coverage, as with Lysenkoism, brands it a pseudoscience without explanation. But YEC makes bold, falsifiable claims about biology and genetics (not merely evolution), geology (plate tectonics or lack thereof), and, most significantly, Newtonian mechanics. While it posits unfalsifiable unobservables including a divinity that sculpts the universe in six days, much of its paradigm contrasts modern physics in testable ways. Creation Science is not a miscarriage of science in the sense of some of the others. I’m covering it here because it has many similarities to other bad sciences and is a great test of demarcation criteria. Creation Science does limited harm because it preaches to the choir. I doubt anyone ever joined a cult because they were persuaded that creationism is scientific.
Intelligent Design
Old-earth creationism, now known as Intelligent Design (ID) theory is much different. While ID could have confined itself to the realm of metaphysics and stayed out of our cross hairs, it did not. ID mostly confines itself to the realm of descriptions and explanations, but it explicitly claims to be a science. Again, Wikipedia brands ID as pseudoscience, and, again, this distinction seems shallow. I’m also concerned that the label is rooted in anti-Christian bias with reasons invented after the labelling as a rationalization. To be clear, I see nothing substantial in ID that is scientific, but its opponents’ arguments are often not much better than those of its proponents.
It might be true that a supreme being, benevolent or otherwise, guided the hand of cosmological and biological evolution. But simpler, adequate explanations of those processes exist outside of ID, and ID adds no explanatory power to the theories of cosmology and biology that are independent of it. This was not always the case. The US founding fathers, often labeled Christian by modern Christians, were not Christian at all. They were deists, mainly because they lacked a theoretical framework to explain the universe without a creator, who had little interest in earthly affairs. They accepted the medieval idea that complex organisms, like complex mechanisms, must have a designer. Emergent complexity wasn’t seen as an option. That they generally – notably excepting David Hume – failed to see the circularity of this “teleological argument” can likely be explained by Kuhn’s notion of the assent of the relevant community. Each of them bought it because they all bought it. It was the reigning paradigm.
While intelligent design could logically be understood to not require a Judeo-Christian god, ID seems to have emerged out of fundamentalist Christian objection to teaching evolution in public schools. Logically, “intelligent design” could equally apply to theories involving a superior but not supreme creator or inventor. Space aliens may have seeded the earth with amino acids – the Zoo Hypothesis. Complex organic molecules could have been sent to earth on a comet by highly advanced – and highly patient – aliens, something we might call directed panspermia. Or we could be living in a computer simulation of an alien school kid. Nevertheless, ID seems to be a Christian undertaking positing a Christian God.
Opponents are quick to point this out. ID is motivated by Christian sentiments and is closely aligned with Christian evangelism. Is this a fair criticism of ID as a science? I tend to think not. Newton was strongly motivated by Christian beliefs, though his religion, something like Arianism or Unitarianism, would certainly be rejected by modern Christians. Regardless, Newton’s religious motivation for his studies no more invalidates them than Linus Pauling’s (covered below) economic motivations invalidate his work. Motivations of practitioners, in my view, cannot be grounds for calling a field of inquiry pseudoscience or bad science. Some social scientists disagree.
Dominated by Negative Arguments
YEC and ID writings focus on arguing that much of modern science, particularly evolutionary biology, cannot be correct. For example, much of YEC’s efforts are directed at arguing that the earth cannot be 4.5 billion years old. Strictly speaking, this ( the theory that another theory is wrong) is a difficult theory to disprove. Most scientists tend to think that disproving a theory that itself aims to disprove geology is pointless. They hold that the confirming evidence for modern geologic theory is sufficient. Karl Popper, who held that absence of disconfirmation was the sole basis for judging a theory good, would seem to have a problem with this though. YEC also holds theories defending a single worldwide flood within the last 5,000 years. That seems reasonably falsifiable, if one accepts a large body of related science including several radioactive dating techniques, mechanics of solids, denudation rate calculations, and much more.
Further, it is flawed reasoning (“false choice”) to think that exposing a failure of classical geology is support for a specific competing theory.
YEC and, perhaps surprisingly, much of ID have assembled a body of negative arguments against Darwinism, geology, and other aspects of a naturalistic worldview. Arguing that fossil evidence is an insufficient basis for evolution and that natural processes cannot explain the complexity of the eyeball are characteristically negative arguments. This raises the question of whether a bunch of negative arguments can rightly be called a science. While Einstein started with the judgement that the wave theory of light could not be right (he got the idea from Maxwell), his program included developing a bold, testable, and falsifiable theory that posited that light was something that came in discreet packages, along with predictions about how it would behave in a variety of extreme circumstances. Einsteinian relativity gives us global positioning and useful tools in our cell phones. Creationism’s utility seems limited to philosophical realms. Is lack of practical utility or observable consequences a good basis for calling an endeavor unscientific? See String Theory, below.
Wikipedia (you might guess that I find Wikipedia great for learning the discography of Miley Cyrus but poor for serious inquiries), appealing to “consensus” and “the scientific community,” judges Creation Science to be pseudoscience because creationism invokes supernatural causes. In the same article, it decries the circular reasoning of ID’s argument from design (the teleological argument). But claiming that Creation Science invokes supernatural causes is equally circular unless we’re able to draw the natural/supernatural distinction independently from the science/pseudoscience distinction. Creationists hold that creation is natural; that’s their whole point.
Ignoring Disconfirming Evidence
YEC proponents seem to refuse to allow that any amount of radioactive dating evidence falsifies their theory. I’m tempted to say this alone makes YEC either a pseudoscience or just terrible science. But doing so would force me to accept the 2nd and 3rd definitions of science that I gave in the previous post. In other words, I don’t want to judge a scientific inquiry’s status (or even the status of a non-scientific one) on the basis of what its proponents (a community or institution) do at an arbitrary point in time. Let’s judge the theory, not its most vocal proponents. A large body of German physicists denied that Edington’s measurement confirmed Einstein’s prediction of bent light rays during an eclipse because they rejected Jewish physics. Their hardheadedness is no reason to call their preferred wave theory of light a bad theory. It was a good theory with bad adherents, a good theory for which we now have excellent reasons to judge wrong.
Some YEC proponents hold that, essentially, the fossil record is God’s little joke. Indeed it is possible that when God created the world in six days a few thousand years ago he laid down a lot of evidence to test our faith. The ancient Christian writer Tertullian argued that Satan traveled backward in time to plant evidence against Christian doctrine (more on him soon). It’s hard to disprove. The possibility of deceptive evidence is related to the worry expressed by Hume and countless science fiction writers that the universe, including fossils and your memories of today’s breakfast, could have been planted five minutes ago. Like the Phantom Time hypothesis, it cannot be disproved. Also, as with Phantom Time, we have immense evidence against it. And from a practical perspective, nothing in the future would change if it were true.
Lakatos Applied to Creation Science
Lakatos might give us the best basis for rejecting Creation Science as pseudoscience rather than as an extraordinarily bad science, if that distinction has any value, which it might in the case of deciding what can be taught in elementary school. (We have no laws against unsuccessful theories or poor science.) Lakatos was interested in how a theory makes use of laws of nature and what its research agenda looks like. Laws of nature are regularities observed in nature so widely that we assume them to be true, contingently, and ground predictions about nature on them. Creation Science usually has little interest in making testable predictions about nature or the universe on the basis of such laws. Dr. Duane Gish of the Institute for Creation Research (ICR) wrote in Evolution, The Fossils Say No that “God used processes which are not now operating anywhere in the natural universe.” This is a major point against Creation Science counting as science.
Creation Science’s lack of testable predictions might not even be a fair basis for judging a pursuit to be unscientific. Botany is far more explanatory than predictive, and few of us, including Wikipedia, are ready to expel botany from the science club.
Most significant for me, Lakatos casts doubt on Creation Science by the thinness of its research agenda. A look at the ICR’s site reveals a list of papers and seminars all by PhDs and MDs. They seem to fall in two categories: evolution is wrong (discussed above), and topics that are plausible but that don’t give support for creationism in any meaningful way. The ploy here is playing a game with the logic of confirmation.
By the Will of Elvis
Consider the following statement of hypothesis. Everything happens by the will of Elvis. Now this statement, if true, logically ensures that the following disjunctive statement is true: Either everything happens by the will of Elvis or all cats have hearts. Now let’s go out with a stethoscope and do some solid cat science to gather empirical evidential support for all cats having hearts. This evidence gives us reasonable confidence that the disjunctive statement is true. Since the original simple hypothesis logically implies the disjunction, evidence that cats have hearts gives support for the hypothesis that everything happens by the will of Elvis. This is a fun game (like Hempel’s crows) in the logic of confirmation, and those who have studied it will instantly see the ruse. But ICR has dedicated half its research agenda to it, apparently to deceive its adherents.
The creationist research agenda is mostly aimed at negating evolution and at large philosophical matters. Where it deals with small and specific scientific questions – analogous to cat hearts in the above example – the answers to those questions don’t in any honest sense provide evidentiary support for divine creation.
If anything fails the test of being valid science, Creation Science does. Yet popular arguments that attempt to logically dismiss it from the sciences seem prejudiced or ill motivated. As discussed in the last post, fair and honest demarcation is not so simple. This may be a case where we have to take the stance of Justice Potter Stewart, who, when judging whether Lady Chatterley’s Lover was pornography, said “I shall not today attempt further to define [it], but I know it when I see it, and this is not it.”
To be continued.
What is a climate denier?
Posted by Bill Storage in Sustainable Energy on September 25, 2019
Climate change denier, climate denial and similar terms peaked in usage, according to Google trends data, at the last presidential election. Usage today is well below those levels, but based on trends in the last week, is heading for a new high. The obvious meaning of climate change denial would seem to me to be saying that either the climate is not changing or that people are not responsible for climate change. But this is clearly not the case.
Patrick Moore, a once influential Greenpeace member, is often called a denier by climate activists. Niall Ferguson says he doesn’t deny anthropogenic climate change, but is attacked as a denier. After a Long Now Foundation talk by Saul Griffith, I heard Saul being accused being a denier. Even centenarian James Lovelock, the originator of Gaia theory who now believes his former position was alarmist (“I’ve grown up a bit since then“), is called a denier in California green energy events, despite his very explicit denial of being a denier.
Trying to look logically at the spectrum of propositions one might affirm or deny, I come up with the following possible claims. You can no doubt fine-tune these or make them more granular.
- The earth’s climate is changing (typically, average temperature is increasing.
- The earth’s average temperature has increased more rapidly since the industrial revolution.
- Some increase in warming rate is caused by human activity.
- The increase in warming rate is overwhelmingly due to humans (as opposed to, e.g. sun activity and orbital factors)
- Anthropogenic warming poses imminent threat to human life on earth.
- The status quo (greenhouse gas production) will result in human extinction.
- The status quo poses significant threat (even existential threat) and the proposed renewables policy will mitigate it.
- Nuclear energy is not an acceptable means of reducing greenhouse gas production.
No one with a command of high school math and English could deny claim 1. Nearly everything is changing at some level. We can argue about what constitutes significant change. That’s a matter of definition, of meaning, and of values.
Claim 2 is arguable. It depends on having a good bit of data. We can argue about data sufficiency, accuracy and interpretation of the noisy data.
Claim 3 relies much more on theory (to establishing causation) than on meaning/definitions and facts/measurements, as is the case with 1 and 2. Claim 4 is a strong version of claim 3, requiring much more scientific analysis and theorizing.
While informed by claims 1-4, Claims 5 and 6 (imminent threat, certain doom) are mostly outside the strict realm of science. They differ on the severity of the threat; and they rely of risk modeling, engineering feasibility analyses, and economics. For example, could we afford to pay for the mitigations that could reverse the effects of continued greenhouse gas release, and is geoengineering feasible? Claim 6 is held by Greta Thunberg (“we are in the beginning of a mass extinction”). Al Gore seems somewhere between 5 and 6.
Claim 7 (renewables can cure climate change) is the belief held by followers of the New Green Deal.
While unrelated to the factual (whether true or false) components of claims 1-4 and the normative components of claims 5-7, claim 8 (fission not an option) seems to be closely aligned with claim 6. Vocal supporters of 6 tend to be proponents of 8. Their connection seems to be on ideological grounds. It seems logically impossible to reconcile holding claims 6 and 8 simultaneously. I.e., neither the probability nor severity components of nuclear risk can exceed claim 6’s probability (certainty) and severity (extinction). Yet they are closely tied. Naomi Oreskes accused James Hansen of being a denier because he endorsed nuclear power.
Beliefs about the claims need not be binary. For each claim, one could hold belief in a range from certitude to slightly possible, as well as unknown or unknowable. Fred Singer, for example, accepts that CO2 alters the climate, but allows that its effect could be cooling rather than warming. Singer’s uncertainty stems from his perception that the empirical data does not jibe with global-warming theory. It’s not that he’s lukewarm; he finds the question presently unknowable. This is a form of denial (see Freedman and McKibben below) green activists, blissfully free of epistemic humility and doubt, find particularly insidious.
Back to the question of what counts as a denier. I once naively thought that “climate change denier” applies only to claims 1-4. After all, the obvious literal meaning of the words would apply only to claims 1 and 2. We can add 3 and 4 if we allow that those using the term climate denier use it as a short form of “anthopogenic climate-change denier.”
Clearly, this is not the popular usage, however. I am regularly called a denier at green-tech events for arguing against claim 7 (renewables as cure). Whether anthopogenic climate change exists, regardless of the size of the threat, wind and solar cannot power a society anything like the one we live in. I’m an engineer, I specialized in thermodynamics and energy conversion, that’s my argument, and I’m happy to debate it.
Green activists’ insistence that we hold claim 8 (no fission) to be certain, in my view, calls their program and motivations into question, for reasons including the above mentioned logical incompatibility of claims 6 and 8 (certain extinction without change, but fission is to dangerous).
I’ve rarely heard anyone deny claims 1-3 (climate change exists and humans play a role). Not even Marc Morano denies these. I don’t think any of our kids, indoctrinated into green policy at school, have any idea that those they’re taught are deniers do not deny climate change.
In the last year I’ve seen a slight increase in professional scientists who deny claim 4 (overwhelmingly human cause), but the majority of scientists in relevant fields seem to agree with claim 4. Patrick Moore, Caleb Rossiter, Roger A. Pielke and Don Easterbrook seem to deny claim 4. Leighton Steward denies it on the grounds that climate change is the cause of rising CO2 levels, not its effect.
Some of the key targets of climate activism don’t appear to deny the basic claims of climate change. Among these are Judith Curry, Richard Tol, Ivar Giaever, Roy Spencer, Robert M Carter, Denis Rancourt, Richard Tol, John Theon, Scott Armstrong, Patrick Michaels, Will Happer and Philip Stott. Anthony Watts and Matt Ridley are very explicit about accepting claim 4 (mostly human-caused) but denying claims 5 and 6 (significant threat or extinction). William M. Briggs called himself a climate denier, but meant by it that the concept of climate, as understood by most people, is itself invalid.
More and more people who disagree with the greens’ proposed policy implementation are labeled deniers (as Oreskes calling Hansen a denier because he supports fission). Andrew Freedman seemed to implicitly acknowledge the expanding use of the denier label in a recent Mashable piece, in which he warned of some green opponents who were moving “from outright climate denial to a more subtle, insidious and risky form.” Bill McKibben, particularly immune to the nuances of scientific method and rational argument, called “renewables denial” “at least as ugly” as climate denial.
Opponents argue that the green movement is a religious cult. Arguing over matters of definition has limited value, but greens are prone to apocalyptic rants that would make Jonathan Edwards blush, focus on sin and redemption, condemnation of heresy, and attempts to legislate right behavior. Last week The Conversation said it was banning not only climate denial but “climate skepticism”). I was amused at an aspect of the religiosity of the greens in both Freedman and McKibben’s complaints.: each is insisting that being partially sinful warrants more condemnation than committing the larger sin.
So because you are lukewarm, and neither hot nor cold, I will spit you out of My mouth. – Revelation 3:16 (NAS)
Refusal to debate crackpots is understandable, but Michael Mann’s refusal to debate “deniers” (he refused even to share his data when order to do so by British Columbia Supreme Court) looks increasingly like fear of engaging worthy opponents – through means other than suing them.
On his liberal use of the “denier” accusation, the below snippet provides some levity. In a house committee session Mann denies calling anyone a denier and says he’s been misrepresented. Judith Curry (the denier) responds “it’s in your written testimony.” On page 6 of Mann’s testimony, he says “climate science denier Judith Curry” adding that “I use the term carefully.”
I deny claims 6 through 8. The threat is not existential; renewables won’t fix it; and fission can.
Follow this proud denier on twitter.
Data without theory is lame
Posted by Bill Storage in History of Science, Philosophy of Science on July 25, 2016
Just over eight years ago Chris Anderson of Wired announced with typical Silicon Valley humility that big data had made the scientific method obsolete. Seemingly innocent of any training in science, Anderson explained that correlation is enough; we can stop looking for models.
Anderson came to mind as I wrote my previous post on Richard Feynman’s philosophy of science and his strong preference for the criterion of explanatory power over the criterion of predictive success in theory choice. By Anderson’s lights, theory isn’t needed at all for inference. Anderson didn’t see his atheoretical approach as non-scientific; he saw it as science without theory.
Anderson wrote:
“…the big target here isn’t advertising, though. It’s science. The scientific method is built around testable hypotheses. These models, for the most part, are systems visualized in the minds of scientists. The models are then tested, and experiments confirm or falsify theoretical models of how the world works. This is the way science has worked for hundreds of years… There is now a better way. Petabytes allow us to say: ‘Correlation is enough.’… Correlation supersedes causation, and science can advance even without coherent models, unified theories, or really any mechanistic explanation at all.”
Anderson wrote that at the dawn of the big data era – now known as machine learning. Most interesting to me, he said not only is it unnecessary to seek causation from correlation, but correlation supersedes causation. Would David Hume, causation’s great foe, have embraced this claim? I somehow think not. Call it irrational data exuberance. Or driving while looking only into the rear view mirror. Extrapolation can come in handy; but it rarely catches black swans.
Philosophers of science concern themselves with the concept of under-determination of theory by data. More than one theory can fit any set of data. Two empirically equivalent theories can be logically incompatible, as Feynman explains in the video clip. But if we remove theory from the picture, and predict straight from the data, we face an equivalent dilemma we might call under-determination of rules by data. Economic forecasters and stock analysts have large collections of rules they test against data sets to pick a best fit on any given market day. Finding a rule that matches the latest historical data is often called fitting the rule on the data. There is no notion of causation, just correlation. As Nassim Nicholas Taleb describes in his writings, this approach can make you look really smart for a time. Then things change, for no apparent reason, because the rule contains no mechanism and no explanation, just like Anderson said.
In Bobby Henderson’s famous Pastafarian Open Letter to Kansas School Board, he noted the strong inverse correlation between global average temperature and the number of seafaring pirates over the last 200 years. The conclusion is obvious; we need more pirates.
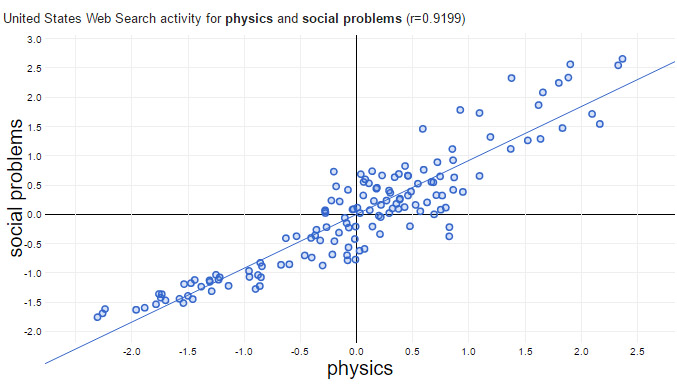
My recent correlation-only research finds positive correlation (r = 0.92) between Google searches on “physics” an “social problems.” It’s just too hard to resist seeking an explanation. And, as positivist philosopher Carl Hempel stressed, explanation is in bed with causality; so I crave causality too. So which is it? Does a user’s interest in physics cause interest in social problems or the other way around? Given a correlation, most of us are hard-coded to try to explain it – does a cause b, does b cause a, does hidden variable c cause both, or is it a mere coincidence?
Big data is a tremendous opportunity for theory-building; it need not supersede explanation and causation. As Sean Carroll paraphrased Kant in The Big Picture:
“Theory without data is blind. Data without theory is lame.”
— — —
[edit 7/28: a lighter continuation of this topic here]
.
Happy is he who gets to know the causes of things – Virgil
Can Science Survive?
Posted by Bill Storage in History of Science, Philosophy of Science on February 16, 2016

In my last post I ended with the question of whether science in the pure sense can withstand science in the corporate, institutional, and academic senses. Here’s a bit more on the matter.
Ronald Reagan, pandering to a church group in Dallas, famously said about evolution, “Well, it is a theory. It is a scientific theory only.” (George Bush, often “quoted” as saying this, did not.) Reagan was likely ignorant of the distinction between two uses of the word, theory. On the street, “theory” means an unsettled conjecture. In science a theory – gravitation for example – is a body of ideas that explains observations and makes predictions. Reagan’s statement fueled years of appeals to teach creationism in public schools, using titles like creation science and intelligent design. While the push for creation science is usually pinned on southern evangelicals, it was UC Berkeley law professor Phillip E Johnson who brought us intelligent design.
Arkansas was a forerunner in mandating equal time for creation science. But its Act 590 of 1981 (Balanced Treatment for Creation-Science and Evolution-Science Act) was shut down a year later by McLean v. Arkansas Board of Education. Judge William Overton made philosophy of science proud with his set of demarcation criteria. Science, said Overton:
- is guided by natural law
- is explanatory by reference to natural law
- is testable against the empirical world
- holds tentative conclusions
- is falsifiable
For earlier thoughts on each of Overton’s five points, see, respectively, Isaac Newton, Adelard of Bath, Francis Bacon, Thomas Huxley, and Karl Popper.
In the late 20th century, religious fundamentalists were just one facet of hostility toward science. Science was also under attack on the political and social fronts, as well an intellectual or epistemic front.
President Eisenhower, on leaving office in 1960, gave his famous “military industrial complex” speech warning of the “danger that public policy could itself become the captive of a scientific technological elite.” At about the same time the growing anti-establishment movements – perhaps centered around Vietnam war protests – vilified science for selling out to corrupt politicians, military leaders and corporations. The ethics of science and scientists were under attack.
Also at the same time, independently, an intellectual critique of science emerged claiming that scientific knowledge necessarily contained hidden values and judgments not based in either objective observation (see Francis Bacon) or logical deduction (See Rene Descartes). French philosophers and literary critics Michel Foucault and Jacques Derrida argued – nontrivially in my view – that objectivity and value-neutrality simply cannot exist; all knowledge has embedded ideology and cultural bias. Sociologists of science ( the “strong program”) were quick to agree.
This intellectual opposition to the methodological validity of science, spurred by the political hostility to the content of science, ultimately erupted as the science wars of the 1990s. To many observers, two battles yielded a decisive victory for science against its critics. The first was publication of Higher Superstition by Gross and Levitt in 1994. The second was a hoax in which Alan Sokal submitted a paper claiming that quantum gravity was a social construct along with other postmodern nonsense to a journal of cultural studies. After it was accepted and published, Sokal revealed the hoax and wrote a book denouncing sociology of science and postmodernism.
Sadly, Sokal’s book, while full of entertaining examples of the worst of postmodern critique of science, really defeats only the most feeble of science’s enemies, revealing a poor grasp of some of the subtler and more valid criticism of science. For example, the postmodernists’ point that experimentation is not exactly the same thing as observation has real consequences, something that many earlier scientists themselves – like Robert Boyle and John Herschel – had wrestled with. Likewise, Higher Superstition, in my view, falls far below what we expect from Gross and Levitt. They deal Bruno Latour a well-deserved thrashing for claiming that science is a completely irrational process, and for the metaphysical conceit of holding that his own ideas on scientific behavior are fact while scientists’ claims about nature are not. But beyond that, Gross and Levitt reveal surprisingly poor knowledge of history and philosophy of science. They think Feyerabend is anti-science, they grossly misread Rorty, and waste time on a lot of strawmen.
Following closely on the postmodern critique of science were the sociologists pursuing the social science of science. Their findings: it is not objectivity or method that delivers the outcome of science. In fact it is the interests of all scientists except social scientists that govern the output of scientific inquiry. This branch of Science and Technology Studies (STS), led by David Bloor at Edinburgh in the late 70s, overplayed both the underdetermination of theory by evidence and the concept of value-laden theories. These scientists also failed to see the irony of claiming a privileged position on the untenability of privileged positions in science. I.e., it is an absolute truth that there are no absolute truths.
While postmodern critique of science and facile politics in STC studies seem to be having a minor revival, the threats to real science from sociology, literary criticism and anthropology (I don’t mean that all sociology and anthropology are non-scientific) are small. But more subtle and possibly more ruinous threats to science may exist; and they come partly from within.
Modern threats to science seem more related to Eisenhower’s concerns than to the postmodernists. While Ike worried about the influence the US military had over corporations and universities (see the highly nuanced history of James Conant, Harvard President and chair of the National Defense Research Committee), Eisenhower’s concern dealt not with the validity of scientific knowledge but with the influence of values and biases on both the subjects of research and on the conclusions reached therein. Science, when biased enough, becomes bad science, even when scientists don’t fudge the data.
Pharmaceutical research is the present poster child of biased science. Accusations take the form of claims that GlaxoSmithKline knew that Helicobacter pylori caused ulcers – not stress and spicy food – but concealed that knowledge to preserve sales of the blockbuster drugs, Zantac and Tagamet. Analysis of those claims over the past twenty years shows them to be largely unsupported. But it seems naïve to deny that years of pharmaceutical companies’ mailings may have contributed to the premature dismissal by MDs and researchers of the possibility that bacteria could in fact thrive in the stomach’s acid environment. But while Big Pharma may have some tidying up to do, its opponents need to learn what a virus is and how vaccines work.
Pharmaceutical firms generally admit that bias, unconscious and of the selection and confirmation sort – motivated reasoning – is a problem. Amgen scientists recently tried to reproduce results considered landmarks in basic cancer research to study why clinical trials in oncology have such high failure rate. They reported in Nature that they were able to reproduce the original results in only six of 53 studies. A similar team at Bayer reported that only about 25% of published preclinical studies could be reproduced. That the big players publish analyses of bias in their own field suggests that the concept of self-correction in science is at least somewhat valid, even in cut-throat corporate science.
Some see another source of bad pharmaceutical science as the almost religious adherence to the 5% (+- 1.96 sigma) definition of statistical significance, probably traceable to RA Fisher’s 1926 The Arrangement of Field Experiments. The 5% false-positive probability criterion is arbitrary, but is institutionalized. It can be seen as a classic case of subjectivity being perceived as objectivity because of arbitrary precision. Repeat any experiment long enough and you’ll get statistically significant results within that experiment. Pharma firms now aim to prevent such bias by participating in a registration process that requires researchers to publish findings, good, bad or inconclusive.
Academic research should take note. As is often reported, the dependence of publishing on tenure and academic prestige has taken a toll (“publish or perish”). Publishers like dramatic and conclusive findings, so there’s a strong incentive to publish impressive results – too strong. Competitive pressure on 2nd tier publishers leads to their publishing poor or even fraudulent study results. Those publishers select lax reviewers, incapable of or unwilling to dispute authors. Karl Popper’s falsification model of scientific behavior, in this scenario, is a poor match for actual behavior in science. The situation has led to hoaxes like Sokal’s, but within – rather than across – disciplines. Publication of the nonsensical “Fuzzy”, Homogeneous Configurations by Marge Simpson and Edna Krabappel (cartoon character names) by the Journal of Computational Intelligence and Electronic Systems in 2014 is a popular example. Following Alan Sokal’s line of argument, should we declare the discipline of computational intelligence to be pseudoscience on this evidence?
Note that here we’re really using Bruno Latour’s definition of science – what scientists and related parties do with a body of knowledge in a network, rather than simply the body of knowledge. Should scientists be held responsible for what corporations and politicians do with their knowledge? It’s complicated. When does flawed science become bad science. It’s hard to draw the line; but does that mean no line needs to be drawn?
Environmental science, I would argue, is some of the worst science passing for genuine these days. Most of it exists to fill political and ideological roles. The Bush administration pressured scientists to suppress communications on climate change and to remove the terms “global warming” and “climate change” from publications. In 2005 Rick Piltz resigned from the U.S. Climate Change Science Program claiming that Bush appointee Philip Cooney had personally altered US climate change documents to lessen the strength of their conclusions. In a later congressional hearing, Cooney confirmed having done this. Was this bad science, or just bad politics? Was it bad science for those whose conclusions had been altered not to blow the whistle?
The science of climate advocacy looks equally bad. Lack of scientific rigor in the IPCC is appalling – for reasons far deeper than the hockey stick debate. Given that the IPCC started with the assertion that climate change is anthropogenic and then sought confirming evidence, it is not surprising that the evidence it has accumulated supports the assertion. Compelling climate models, like that of Rick Muller at UC Berkeley, have since given strong support for anthropogenic warming. That gives great support for the anthropogenic warming hypothesis; but gives no support for the IPCC’s scientific practices. Unjustified belief, true or false, is not science.
Climate change advocates, many of whom are credentialed scientists, are particularly prone to a mixing bad science with bad philosophy, as when evidence for anthropogenic warming is presented as confirming the hypothesis that wind and solar power will reverse global warming. Stanford’s Mark Jacobson, a pernicious proponent of such activism, does immeasurable damage to his own stated cause with his descent into the renewables fantasy.
Finally, both major climate factions stoop to tying their entire positions to the proposition that climate change has been measured (or not). That is, both sides are in implicit agreement that if no climate change has occurred, then the whole matter of anthropogenic climate-change risk can be put to bed. As a risk man observing the risk vector’s probability/severity axes – and as someone who buys fire insurance though he has a brick house – I think our science dollars might be better spent on mitigation efforts that stand a chance of being effective rather than on 1) winning a debate about temperature change in recent years, or 2) appeasing romantic ideologues with “alternative” energy schemes.
Science survived Abe Lincoln (rain follows the plow), Ronald Reagan (evolution just a theory) and George Bush (coercion of scientists). It will survive Barack Obama (persecution of deniers) and Jerry Brown and Al Gore (science vs. pronouncements). It will survive big pharma, cold fusion, superluminal neutrinos, Mark Jacobson, Brian Greene, and the Stanford propaganda machine. Science will survive bad science because bad science is part of science, and always has been. As Paul Feyerabend noted, Galileo routinely used propaganda, unfair rhetoric, and arguments he knew were invalid to advance his worldview.
Theory on which no evidence can bear is religion. Theory that is indifferent to evidence is often politics. Granting Bloor, for sake of argument, that all theory is value-laden, and granting Kuhn, for sake of argument, that all observation is theory-laden, science still seems to have an uncanny knack for getting the world right. Planes fly, quantum tunneling makes DVD players work, and vaccines prevent polio. The self-corrective nature of science appears to withstand cranks, frauds, presidents, CEOs, generals and professors. As Carl Sagan Often said, science should withstand vigorous skepticism. Further, science requires skepticism and should welcome it, both from within and from irksome sociologists.
.
.
XKCD cartoon courtesy of xkcd.com
The Trouble with Strings
Posted by Bill Storage in History of Science, Philosophy of Science on February 1, 2016
Theoretical physicist Brian Greene is brilliant, charming, and silver-tongued. I’m guessing he’s the only Foundational Questions Institute grant awardee who also appears on the Pinterest Gorgeous Freaking Men page. Greene is the reigning spokesman for string theory, a theoretical framework proposing that one dimensional (also higher dimensions in later variants, e.g., “branes”) objects manifest different vibrational modes to make up all particles and forces of physics’ standard model. Though its proponents now discourage such usage, many call string theory the grand unification, the theory of everything. Since this includes gravity, string theorists also hold that string theory entails the elusive theory of quantum gravity. String theory has gotten a lot of press over the past few decades in theoretical physics and, through academic celebrities like Greene, in popular media.

Several critics, some of whom once spent time in string theory research, regard it as not a theory at all. They see it as a mere formalism – a potential theory or family – very, very large family – of potential theories, all of which lack confirmable or falsifiable predictions. Lee Smolin, also brilliant, lacks some of Greene’s other attractions. Smolin is best known for his work in loop quantum gravity – roughly speaking, string theory’s main competitor. Smolin also had the admirable nerve to publicly state that, despite the Sokol hoax affair, sociologists have the right and duty to examine the practice of science. His sensibilities on that issue bring to bear on the practice of string theory.
Columbia University’s Peter Woit, like Smolin, is a highly vocal critic of string theory. Like Greene and Smolin, Woit is wicked sharp, but Woit’s tongue is more venom than silver. His barefisted blog, Not Even Wrong, takes its name from a statement Rudolf Peierls claimed Wolfgang Pauli had made about some grossly flawed theory that made no testable predictions.
The technical details of whether string theory is in fact a theory or whether string theorists have made testable predictions or can, in theory, ever make such predictions is great material that one could spend a few years reading full time. Start with the above mentioned authors and follow their references. Though my qualifications to comment are thin, it seems to me that string theory is at least in principle falsifiable, at least if you accept that failure to detect supersymmetry (required for strings) at the LHC or future accelerators over many attempts to do so.
But for this post I’m more interested in a related topic that Woit often covers – not the content of string theory but its practice and its relationship to society.
Regardless of whether it is a proper theory, through successful evangelism by the likes of Greene, string theory has gotten a grossly disproportionate amount of research funding. Is it the spoiled, attention-grabbing child of physics research? A spoiled child for several decades, says Woit – one that deliberately narrowed the research agenda to exclude rivals. What possibly better theory has never seen the light of day because its creator can’t get a university research position? Does string theory coerce and persuade by irrational methods and sleight of hand, as Feyerabend argued was Galileo’s style? Galileo happened to be right of course – at least on some major points.
Since Galileo’s time, the practice of science and its relationship to government, industry, and academic institutions has changed greatly. Gentleman scientists like Priestly, Boyle, Dalton and Darwin are replaced by foundation-funded university research and narrowly focused corporate science. After Kuhn – or misusing Kuhn – sociologists of science in the 1980s and 90s tried to knock science from its privileged position on the grounds that all science is tainted with cultural values and prejudices. These attacks included claims of white male bias and echoes of Eisenhower’s warnings about the “military industrial complex.” String theory, since it holds no foreseeable military or industrial promise, would seem to have immunity from such charges of bias. I doubt Democrats like string more than Republicans.
Yet, as seen by Smolin and Woit, in string theory, Kuhn’s “relevant community” became the mob (see Lakatos on Kuhn/mob) – or perhaps a religion not separated from the state. Smolin and Woit point to several cult aspects of the string theory community. They find it to be cohesive, monolithic and high-walled – hard both to enter and to leave. It is hierarchical; a few leaders control the direction of the field while its initiates aim to protect the leaders from dissenting views. There is an uncommon uniformity of views on open questions; and evidence is interpreted optimistically. On this view, string theorists yield to Bacon’s idols of the tribe, the cave, and the marketplace. Smolin cites the rarity of particle physicists outside of string theory to be invited to its conferences.
In The Trouble with Physics, Smolin details a particular example of community cohesiveness unbecoming to science. Smolin says even he was, for much of two decades, sucked into the belief that string theory had been proved finite. Only when he sought citations for a historical comparison of approaches in particle physics he was writing did he find that what he and everyone else assumed to have been proved long ago had no basis. He questioned peers, finding that they too had ignored vigorous skepticism and merely gone with the flow. As Smolin tells it, everyone “knew” that Stanley Mandelstam (UC Berkeley) had proved string theory finite in its early days. Yet Mandelstam himself says he did not. I’m aware that there are other takes on the issue of finitude that may soften Smolin’s blow; but, in my view, his point on group cohesiveness and their indignation at being challenged still stand.
A telling example of the tendency for string theory to exclude rivals comes from a 2004 exchange on the sci.physics.strings Google group between Luboš Motl and Wolfgang Lerche of CERN, who does a lot of work on strings and branes. Motl pointed to Leonard Susskind’s then recent embrace of “landscapes,” a concept Susskind had dismissed before it became useful to string theory. To this Lerche replied:
“what I find irritating is that these ideas are out since the mid-80s… this work had been ignored (because it didn’t fit into the philosophy at the time) by the same people who now re-“invent” the landscape, appear in journals in this context and even seem to write books about it. There had always been proponents of this idea, which is not new by any means.. . . the whole discussion could (and in fact should) have been taken place in 1986/87. The main thing what has changed since then is the mind of certain people, and what you now see is the Stanford propaganda machine working at its fullest.”
Can a science department in a respected institution like Stanford in fairness be called a propaganda machine? See my take on Mark Jacobson’s science for my vote. We now have evidence that science can withstand religion. The question for this century might be whether science, in the purse sense, can withstand science in the corporate, institutional, and academic sense.
______________________________
String theory cartoon courtesy of XKCD.
______________________________
I just discovered on Woit’s Not Even Wrong a mention of John Horgan’s coverage of Bayesian belief (previous post) applied to string theory. Horgan notes:
“In many cases, estimating the prior is just guesswork, allowing subjective factors to creep into your calculations. You might be guessing the probability of something that–unlike cancer—does not even exist, such as strings, multiverses, inflation or God. You might then cite dubious evidence to support your dubious belief. In this way, Bayes’ theorem can promote pseudoscience and superstition as well as reason.
Embedded in Bayes’ theorem is a moral message: If you aren’t scrupulous in seeking alternative explanations for your evidence, the evidence will just confirm what you already believe.”
My Trouble with Bayes
Posted by Bill Storage in Philosophy of Science, Probability and Risk, Uncategorized on January 21, 2016
 In past consulting work I’ve wrestled with subjective probability values derived from expert opinion. Subjective probability is an interpretation of probability based on a degree of belief (i.e., hypothetical willingness to bet on a position) as opposed a value derived from measured frequencies of occurrences (related posts: Belief in Probability, More Philosophy for Engineers). Subjective probability is of interest when failure data is sparse or nonexistent, as was the data on catastrophic loss of a space shuttle due to seal failure. Bayesianism is one form of inductive logic aimed at refining subjective beliefs based on Bayes Theorem and the idea of rational coherence of beliefs. A NASA handbook explains Bayesian inference as the process of obtaining a conclusion based on evidence, “Information about a hypothesis beyond the observable empirical data about that hypothesis is included in the inference.” Easier said than done, for reasons listed below.
In past consulting work I’ve wrestled with subjective probability values derived from expert opinion. Subjective probability is an interpretation of probability based on a degree of belief (i.e., hypothetical willingness to bet on a position) as opposed a value derived from measured frequencies of occurrences (related posts: Belief in Probability, More Philosophy for Engineers). Subjective probability is of interest when failure data is sparse or nonexistent, as was the data on catastrophic loss of a space shuttle due to seal failure. Bayesianism is one form of inductive logic aimed at refining subjective beliefs based on Bayes Theorem and the idea of rational coherence of beliefs. A NASA handbook explains Bayesian inference as the process of obtaining a conclusion based on evidence, “Information about a hypothesis beyond the observable empirical data about that hypothesis is included in the inference.” Easier said than done, for reasons listed below.
Bayes Theorem itself is uncontroversial. It is a mathematical expression relating the probability of A given that B is true to the probability of B given that A is true and the individual probabilities of A and B:
P(A|B) = P(B|A) x P(A) / P(B)
If we’re trying to confirm a hypothesis (H) based on evidence (E), we can substitute H and E for A and B:
P(H|E) = P(E|H) x P(H) / P(E)
To be rationally coherent, you’re not allowed to believe the probability of heads to be .6 while believing the probability of tails to be .5; the sum of chances of all possible outcomes must sum to exactly one. Further, for Bayesians, the logical coherence just mentioned (i.e., avoidance of Dutch book arguments) must hold across time (synchronic coherence) such that once new evidence E on a hypothesis H is found, your believed probability for H given E should equal your prior conditional probability for H given E.
Plenty of good sources explain Bayesian epistemology and practice far better than I could do here. Bayesianism is controversial in science and engineering circles, for some good reasons. Bayesianism’s critics refer to it as a religion. This is unfair. Bayesianism is, however, like most religions, a belief system. My concern for this post is the problems with Bayesianism that I personally encounter in risk analyses. Adherents might rightly claim that problems I encounter with Bayes stem from poor implementation rather than from flaws in the underlying program. Good horse, bad jockey? Perhaps.
Problem 1. Subjectively objective
Bayesianism is an interesting mix of subjectivity and objectivity. It imposes no constraints on the subject of belief and very few constraints on the prior probability values. Hypothesis confirmation, for a Bayesian, is inherently quantitative, but initial hypotheses probabilities and the evaluation of evidence is purely subjective. For Bayesians, evidence E confirms or disconfirms hypothesis H only after we establish how probable H was in the first place. That is, we start with a prior probability for H. After the evidence, confirmation has occurred if the probability of H given E is higher than the prior probability of H, i.e., P(H|E) > P(H). Conversely, E disconfirms H when P(H|E) < P(H). These equations and their math leave business executives impressed with the rigor of objective calculation while directing their attention away from the subjectivity of both the hypothesis and its initial prior.
2. Rational formulation of the prior
Problem 2 follows from the above. Paranoid, crackpot hypotheses can still maintain perfect probabilistic coherence. Excluding crackpots, rational thinkers – more accurately, those with whom we agree – still may have an extremely difficult time distilling their beliefs, observations and observed facts of the world into a prior.
3. Conditionalization and old evidence
This is on everyone’s short list of problems with Bayes. In the simplest interpretation of Bayes, old evidence has zero confirming power. If evidence E was on the books long ago and it suddenly comes to light that H entails E, no change in the value of H follows. This seems odd – to most outsiders anyway. This problem gives rise to the game where we are expected to pretend we never knew about E and then judge how surprising (confirming) E would have been to H had we not know about it. As with the general matter of maintaining logical coherence required for the Bayesian program, it is extremely difficult to detach your knowledge of E from the rest of your knowing about the world. In engineering problem solving, discovering that H implies E is very common.
4. Equating increased probability with hypothesis confirmation.
My having once met Hillary Clinton arguably increases the probability that I may someday be her running mate; but few would agree that it is confirming evidence that I will do so. See Hempel’s raven paradox.
5. Stubborn stains in the priors
Bayesians, often citing success in the business of establishing and adjusting insurance premiums, report that the initial subjectivity (discussed in 1, above) fades away as evidence accumulates. They call this washing-out of priors. The frequentist might respond that with sufficient evidence your belief becomes irrelevant. With historical data (i.e., abundant evidence) they can calculate P of an unwanted event in a frequentist way: P = 1-e to the power -RT, roughly, P=RT for small products of exposure time T and failure rate R (exponential distribution). When our ability to find new evidence is limited, i.e., for modeling unprecedented failures, the prior does not get washed out.
6. The catch-all hypothesis
The denominator of Bayes Theorem, P(E), in practice, must be calculated as the sum of the probability of the evidence given the hypothesis plus the probability of the evidence given not the hypothesis:
P(E) = [P(E|H) x p(H)] + [P(E|~H) x P(~H)]
But ~H (“not H”) is not itself a valid hypothesis. It is a family of hypotheses likely containing what Donald Rumsfeld famously called unknown unknowns. Thus calculating the denominator P(E) forces you to pretend you’ve considered all contributors to ~H. So Bayesians can be lured into a state of false choice. The famous example of such a false choice in the history of science is Newton’s particle theory of light vs. Huygens’ wave theory of light. Hint: they are both wrong.
7. Deference to the loudmouth
This problem is related to no. 1 above, but has a much more corporate, organizational component. It can’t be blamed on Bayesianism but nevertheless plagues Bayesian implementations within teams. In the group formulation of any subjective probability, normal corporate dynamics govern the outcome. The most senior or deepest-voiced actor in the room drives all assignments of subjective probability. Social influence rules and the wisdom of the crowd succumbs to a consensus building exercise, precisely where consensus is unwanted. Seidenfeld, Kadane and Schervish begin “On the Shared Preferences of Two Bayesian Decision Makers” with the scholarly observation that an outstanding challenge for Bayesian decision theory is to extend its norms of rationality from individuals to groups. Their paper might have been illustrated with the famous photo of the exploding Challenger space shuttle. Bayesianism’s tolerance of subjective probabilities combined with organizational dynamics and the shyness of engineers can be a recipe for disaster of the Challenger sort.
All opinions welcome.
Science, God, and the White House
Posted by Bill Storage in Philosophy of Science on January 9, 2016
Back in the 80s I stumbled upon the book, Scientific Proof of the Existence of God Will Soon Be Announced by the White House!, by Franklin Jones, aka Frederick Jenkins, later Da Free John, later Adi Da Samraj. I bought it on the spot. Likely a typical 70s mystic charlatan, Jones nonetheless saw clearly our poor grasp of tools for seeking truth and saw how deep and misguided is our deference to authority. At least that’s how I took it.
Who’d expect a hippie mystic to be a keen philosopher of science. The book’s title, connecting science, church and state, shrewdly wraps four challenging ideas:
- That there can be such a thing as scientific proof of anything
- That there could be new findings about the existence of God
- That evidence for God could be in the realm of science
- That government should or could accredit a scientific theory
On the first point, few but the uneducated, TIME magazine, and the FDA think that proof is in the domain of science. Proof is deductive. It belongs to math, logic and analytic philosophy. Science uses evidence and induction to make inferences to the best explanation.
Accepting that strong evidence would suffice as proof, point number 2 is a bit trickier. Evidence of God’s existence can’t be ruled out a priori. God could be observable or detectable; we might see him or his consequences. An almighty god could easily have chosen to regularly show himself or to present unambiguous evidence. But Yahweh, at least in modern times, doesn’t play like that (A wicked and adulterous generation demands a sign but none will be given – Matthew 16:4). While believers often say no evidence would satisfy the atheist, I think a focused team could come up with rules for a demonstration that at least some nonbelievers would accept as sufficient evidence.
Barring any new observations that would constitute evidence, point number 3 is tough to tackle without wading deep into philosophy of science. To see why, consider the theory that God exists. Is it even a candidate for a scientific theory, as one WSJ writer thinks (Science Increasingly Makes the Case for God)? I.e., is it the content of a theory or the way it is handled by its advocates that makes the theory scientific? If the latter, it can be surprisingly hard to draw the line between scientific investigations and philosophical ones. Few scientists admit this line is so blurred, but how do string theorists, who make no confirmable or falsifiable predictions, defend that they are scientists? Their fondness for non-empirical theory confirmation puts them squarely in the ranks of the enlightenment empiricist, Bishop Berkeley of Cloyne (namesake of our fair university) who maintained that matter does not exist. Further, do social scientists make falsifiable predictions, or do they just continually adjust their theory to accommodate disconfirming evidence?
That aside, those who work in the God-theory space somehow just don’t seem to qualify as scientific – even the young-earth creationists trained in biology and geology. Their primary theory doesn’t seem to generate research and secondary theories to confirm or falsify. Their papers are aimed at the public, not peers – and mainly aim at disproving evolution. Can a scientific theory be primarily negative? Could plate-tectonics-is-wrong count as a proper scientific endeavor?
Gould held that God was simply outside the realm of science. But if we accept that the existence of God could be a valid topic of science, is it a good theory? Following Karl Popper, a scientific theory can withstand only a few false predictions. On that view the repeated failures of end-of-days predictions by Harold Camping and Herbert Armstrong might be sufficient to kill the theory of God’s existence. Or does their predictive failures simply exclude them from the community of competent practitioners?
Would NASA engineer, Edgar Whisenant be more credible at making predictions based on the theory of God’s existence? All his predictions of rapture also failed. He was accepted by the relevant community (“…in paradigm choice there is no standard higher than the assent of the relevant community” – Thomas Kuhn) since the Trinity Broadcast Network interrupted its normal programming to help watchers prepare. If a NASA engineer has insufficient scientific clout, how about our first scientist? Isaac Newton predicted, in Observations upon the Prophecies of Daniel and the Apocalypse of St. John, that the end would come in 2000 CE. Maybe Newton’s calculator had the millennium bug.
If we can’t reject the theory for any number of wrong predictions, might there be another basis for rejecting it? Some say absence of a clear mechanism is a good reason to reject theories. In the God theory, no one seems to have proposed a mechanism by which such a God could have arisen. Aquinas’s tortured teleology and Anselm’s ontological arguments still fail on this count. But it seems unfair to dismiss the theory of God’s existence on grounds of no clear mechanism, because we have long tolerated other theories deemed scientific with the same weakness. Gravity, for example.
Does assent of the relevant community grant scientific status to a theory, as Kuhn would have it? If so, who decides which community is the right one? Theologians spend far more time on Armageddon than do biologists and astrophysicists – and theologians are credentialed by their institutions. So why should Hawking and Dawkins get much air time on the matter? Once we’ve identified a relevant community, who gets to participate in its consensus?
This draws in point number 4, above. Should government or the White House have any more claim to a scientific pronouncement than the Council of Bishops? If not, what are we to think of the pronouncements by Al Gore and Jerry Brown that the science of climate is settled? Should they have more clout on the matter than Pope Francis (who, interestingly, has now made similar pronouncements)?
If God is outside the realm of science, should science be outside the jurisdiction of government? What do we make of President Obama’s endorsement of “calling out climate change deniers, one by one”? You don’t have to be Franklin Jones or Da Free John to see signs here of government using the tools of religion (persecution, systematic effort to censure and alienate dissenters) in the name of science. Is it a stretch to see a connection to Jean Bodin, late 16th century French jurist, who argued that only witches deny the existence of witches?
Can you make a meaningful distinction between our government’s pronouncements on the truth or settledness of the climate theory (as opposed to government’s role in addressing it) and the Kremlin’s 1948 pronouncement that only Lamarckian inheritance would be taught, and their call for all geneticists to denounce Mendelian inheritance? Is it scientific behavior for a majority in a relevant community to coerce dissenters?
In trying to draw a distinction between UN and US coercion on climate science and Lysenkoism, some might offer that we (we moderns or we Americans) are somehow different – that only under regimes like Lenin’s and Hitler’s does science get so distorted. In thinking this, it’s probably good to remember that Hitler’s eugenics was born right here, and flourished in the 20th century. It had nearly full academic support in America, including Stanford and Harvard. That is, to use Al Gore’s words, the science was settled. California, always a trendsetter, by the early 1920s, claimed 80% of America’s forced sterilizations. Charles Goethe, founder of Sacramento State University, after visiting Hitler’s Germany in 1934 bragged to a fellow California eugenicist about their program’s influence on Hitler.
If the era of eugenics seems too distant to be relevant to the issue of climate science/politics, consider that living Stanford scientist, Paul Ehrlich, who endorsed compulsory abortion in the 70s, has had a foot in both camps.
As crackpots go, Da Free John was rather harmless.
________
“Indeed, it has been concluded that compulsory population-control laws, even including laws requiring compulsory abortion, could be sustained under the existing Constitution if the population crisis became sufficiently severe to endanger the society.” – Ehrlich, Holdren and Ehrlich, EcoScience, 3rd edn, 1977, p. 837
“You will be interested to know that your work has played a powerful part in shaping the opinions of the group of intellectuals who are behind Hitler in this epoch-making program.” – Charles Goethe, letter to Edwin Black, 1934
Fine Tuned Fibs for the Cause
Posted by Bill Storage in Philosophy of Science on January 7, 2016
In my last post I compared our self-policing of facts that might chip away at our beliefs about environmental religion to lying for God in medieval and ancient times – something the writer of the epistles seems to boast of doing. Lying for God, on matters of science, may still be with us today.
William Lane Craig argues, in a line of thinking he calls reasonable faith (see his video), that the apparent fine tuning of the universe allowing life in it to exist can only be explained as the work a designer. For Craig that designer happens to be the God of evangelical Protestantism.
Fine tuning has two different but related meanings in physics. The first deals mainly with theory, the second mainly with observation – something for Descartes, and something for Bacon.
In theory selection, fine tuning refers to how the details of a theory might need to be tweaked to make them fit observations. For example, in Ptolemaic astronomy, as used prior to Copernicus, the model only matched measurements if the planets’ epicycles stayed put in comparison to the straight line connecting the earth and sun and if the periods of the epicycles were exactly one year. Given those restrictions, the Ptolemaic model made good predictions. But why would those particular quantities have such relations? No reason could be found other than that they needed to be that way for the model to work. In Ptolemy’s defense, he did not believe the model represented reality; it merely gave right predictions. But the church believed it; and they forbade the teaching of the Copernican model. Copernicus’s model gave no better predictions; and it didn’t explain the lack of parallax in star positions or why a rotating earth didn’t suffer from great winds. But, Copernicus didn’t rely on fine tuning of his theory. What criterion is most important in theory selection – absence of fine tuning, predictive success, or explanatory power? That’s a topic for another time I guess. Read Paul Feyerabend on the matter if it grabs you.
In modern physics, fine tuning more commonly refers to our observation that many of the measured values that are, to our knowledge, constant across the universe have values that, were they even slightly different, would prevent life from being possible anywhere. Martin Rees, perhaps the first scientist to delve deep into the matter, identified six dimensionless constants (ratios of things we measure in physics, basically) on which life as we know it depends. These include the ratio of electromagnetic strength to the strength of gravity, the ratio of the mass density of the universe to the density required to halt expansion, and the so-called cosmological constant, the ratio of dark energy density in the universe to the density that would be needed to halt its expansion.
Popular examples of such fine tuning include the claim that if the electromagnetism/gravity ratio differed by an almost infinitesimal amount – say 1 part in 10 to the 40th power (1E-40) – things would be very quiet indeed. With a bit more gravity, stars would be too small and would burn out far too fast. Tweaking the other constants makes things even worse. Adjusting the cosmological constant to a few parts in ten to the 120 in either direction would make the universe either expand too fast for galaxies and stars to form or to collapse upon itself just after the big bang. These are unimaginably large/small numbers. A few scientists argue that our thinking is wrong here – again a topic for later. If interested, see Why the Universe Is Not Designed for Us by Victor J. Stenger.
William Lane Craig accepts that fine tuning exists, giving three possible explanations: physical necessity, chance, or design. Craig rules out necessity because a life-prohibiting universe is easily imaginable. He notes that the probabilities for these incredibly fine-tuned values to occur by chance is ridiculously remote, thus leaving design as the only alternative.
Now I can’t know Craig’s motives or his state of mind, but his argument here is consistent with someone who knows more than he’s telling. That is, Craig is clearly highly intelligent; he has command of analytic philosophy, mathematics and at least a decent knowledge of physics. Yet he starts his fine tuning evangel with an egregious example of privileged hypothesis on top of false choice – just to start. Is he sure the given alternatives are the only live options? And can chance be ruled out in a multiverse model? I.e., in a model with 10 to the 500 instances of what we call our universe, you’re pretty much bound to get a few that look like ours with randomized values for the physical constants.
But we need not start with an exotic option. Did Craig rule out combinations of necessity and chance? Did he challenge the problem statement from the beginning? Many other have – questioning the notion that these measure values aren’t environmental constants at all; perhaps we’ve misconceived an underlying relationship that ties the values together in the same way pi is tied to 3.141592. Part of Stenger’s work is along these lines.
Having given his rationale for preferring the designer hypothesis to an artificially restricted set of alternatives, Craig then takes the leap from designer to the God of evangelical Christianity. That is, Krishna, Zeus, Ahura Mazda and the spaghetti monster are off the table. Craig holds that a being with unlimited cosmic power – who could construct any universe of his choosing – used his infinite powers to fine tune that universe to the precise values of constants that would allow that universe to support galaxies, stars and life. It’s hard for me to believe Craig doesn’t see the contradiction in an argument involving a God of ultimate power being bound by laws of physics. That is, Craig’s God is praiseworthy for essentially outwitting – by a tiny margin – physical laws that are nearly out of his control. This seems a better argument for the religion of the Assyrians than for evangelical Christianity; it recalls Marduk’s narrow defeat over Tiamat.
In Reasonable Faith, Craig deals often with the concept of insincere arguments. Do his religious convictions cause him to be blind to elementary fallacies and contradictions in his own doctrine? Or is he simply lying for the cause?
“…unbelief is at root a spiritual, not an intellectual, problem.” – William Lane Craig, Reasonable Faith: Christian Truth and Apologetics, 3rd edn., p.59
Marcus Vitruvius’s Science
Posted by Bill Storage in Engineering, Philosophy of Science on June 26, 2015
Science, as an enterprise that acquires knowledge and justified beliefs in the form of testable predictions by systematic iterations of observation and math-based theory, started around the 17th century, somewhere between Copernicus and Newton. That, we learned in school, was the beginning of the scientific revolution. Historians of science tend to regard this great revolution as the one that never happened. That is, as Floris Cohen puts it, the scientific revolution, once an innovative and inspiring concept, has since turned into a straight-jacket. Picking this revolution’s starting point, identifying any cause for it, and deciding what concepts and technological innovations belong to it are problematic.
That said, several writers have made good cases for why the pace of evolution – if not revolution – of modern science accelerated dramatically in Europe, only when it did, why it has continuously gained steam rather than petering out, its primary driving force, and the associated transformations in our view of how nature works. Some thought the protestant ethic and capitalism set the stage for science. Others thought science couldn’t emerge until the alliance between Christianity and Aristotelianism was dissolved. Moveable type and mass production of books can certainly claim a role, but was it really a prerequisite? Some think a critical mass of ancient Greek writings had to have been transferred to western Europe by the Muslims. The humanist literary critics that enabled repair and reconstruction of ancient texts mangled in translation from Greek to Syriac to Persian to Latin and botched by illiterate medieval scribes certainly played a part. If this sounds like a stretch, note that those critics seem to mark the first occurrence of a collective effort by a group spread across a large geographic space using shared standards to reach a peer-reviewed consensus – a process sharing much with modern science.
But those reasons given for the scientific revolution all have the feel of post hoc theorizing. Might intellectuals of the day, observing these events, have concluded that a resultant scientific revolution was on the horizon? Francis Bacon comes closest to fitting this bill, but his predictions gave little sense that he was envisioning anything like what really happened.
I’ve wondered why the burst of progress in science – as differentiated from plain know-how, nature-knowledge, art, craft, technique, or engineering knowledge – didn’t happen earlier. Why not just after the period of innovation in from about 1100 to 1300 CE in Europe. In this period Jean Buridan invented calculators and almost got the concept of inertia right. Robert Grosseteste hinted at the experiment-theory model of science. Nicole Oresme debunked astrology and gave arguments for a moving earth. But he was the end of this line. After this brief awakening, which also included the invention of banking and the university, progress came to a screeching halt. Some blame the plague, but that can’t be the culprit. Literature of the time barley mentions the plague. Despite the death toll, politics and war went on as usual; but interest in resurrecting ancient Greek knowledge of all sorts tanked.
Why not in the Islamic world in the time of Ali al-Qushji and al-Birjandi? Certainly the mental capacity was there. A layman would have a hard time distinguishing al-Birjandi’s arguments and thought experiments for the earth’s rotation from those of Galileo. But Islamic civilization at the time had plenty of scholars but no institutions for making practical use of such knowledge and its society would not have tolerated displacement of received wisdom by man-made knowledge.
The most compelling case for civilization having been on the brink of science at an earlier time seems to be the late republic or early imperial Rome. This may seem a stretch, since Rome is much more known for brute force than for finesse, despite their flying buttresses, cranes, fire engines, central heating and indoor plumbing.
 Consider the writings of one Vitruvius, likely Marcus Vitruvius Pollio, in the early reign of Augustus. Vitruvius wrote De Architectura, a ten volume guide to Roman engineering knowledge. Architecture, in Latin, translates accurately into what we call engineering. Rediscovered and widely published during the European renaissance as a standard text for engineers, Vitruvius’s work contains text that seems to contradict what we were all taught about the emergence of the – or a – scientific method.
Consider the writings of one Vitruvius, likely Marcus Vitruvius Pollio, in the early reign of Augustus. Vitruvius wrote De Architectura, a ten volume guide to Roman engineering knowledge. Architecture, in Latin, translates accurately into what we call engineering. Rediscovered and widely published during the European renaissance as a standard text for engineers, Vitruvius’s work contains text that seems to contradict what we were all taught about the emergence of the – or a – scientific method.
Vitruvius is full of surprises. He acknowledges that he is not a scientist (an anachronistic but fitting term) but a collator of Greek learning from several preceding centuries. He describes vanishing point perspective: “…the method of sketching a front with the sides withdrawing into the background, the lines all meeting in the center of a circle.” (See photo below of a fresco in the Oecus at Villa Poppea, Oplontis showing construction lines for vanishing point perspective.) He covers acoustic considerations for theater design, explains central heating technology, and the Archimedian water screw used to drain mines. He mentions a steam engine, likely that later described by Hero of Alexandria (aeolipile drawing at right), which turns heat into rotational energy. He describes a heliocentric model passed down from ancient Greeks. To be sure, there is also much that Vitruvius gets wrong about physics. But so does Galileo.

Most of De Architectura is not really science; it could more accurately be called know-how, technology, or engineering knowledge. Yet it’s close. Vitruvius explains the difference between mere machines, which let men do work, and engines, which derive from ingenuity and allow storing energy.
What convinces me most that Vitruvius – and he surely could not have been alone – truly had the concept of modern scientific method within his grasp is his understanding that a combination of mathematical proof (“demonstration” in his terms) plus theory, plus hands-on practice are needed for real engineering knowledge. Thus he says that what we call science – theory plus math (demonstration) plus observation (practice) – is essential to good engineering.
The engineer should be equipped with knowledge of many branches of study and varied kinds of learning, for it is by his judgement that all work done by the other arts is put to test. This knowledge is the child of practice and theory. Practice is the continuous and regular exercise of employment where manual work is done with any necessary material according to the design of a drawing. Theory, on the other hand, is the ability to demonstrate and explain the productions of dexterity on the principles of proportion.
It follows, therefore, that engineers who have aimed at acquiring manual skill without scholarship have never been able to reach a position of authority to correspond to their pains, while those who relied only upon theories and scholarship were obviously hunting the shadow, not the substance. But those who have a thorough knowledge of both, like men armed at all points, have the sooner attained their object and carried authority with them.
It appears, then, that one who professes himself an engineer should be well versed in both directions. He ought, therefore, to be both naturally gifted and amenable to instruction. Neither natural ability without instruction nor instruction without natural ability can make the perfect artist. Let him be educated, skillful with the pencil, instructed in geometry, know much history, have followed the philosophers with attention, understand music, have some knowledge of medicine, know the opinions of the jurists, and be acquainted with astronomy and the theory of the heavens. – Vitruvius – De Architectura, Book 1
Historians, please correct me if you know otherwise, but I don’t think there’s anything else remotely like this on record before Isaac Newton – anything in writing that comes this close to an understanding of modern scientific method.
So what went wrong in Rome? Many blame Christianity for the demise of knowledge in Rome, but that is not the case here. We can’t know for sure, but the later failure of science in the Islamic world seems to provide a clue. Society simply wasn’t ready. Vitruvius and his ilk may have been ready for science, but after nearly a century of civil war (starting with the Italian social wars), Augustus, the senate, and likely the plebes, had seen too much social innovation that all went bad. The vision of science, so evident during the European Enlightenment, as the primary driver of social change, may have been apparent to influential Romans as well, at a time when social change had lost its luster. As seen in writings of Cicero and the correspondence between Pliny and Trajan, Rome now regarded social innovation with suspicion if not contempt. Roman society, at least its government and aristocracy, simply couldn’t risk the main byproduct of science – progress.
———————————-
History is not merely what happened: it is what happened in the context of what might have happened. – Hugh Trevor-Roper – Oxford Valedictorian Address, 1998
The affairs of the Empire of letters are in a situation in which they never were and never will be again; we are passing now from an old world into the new world, and we are working seriously on the first foundation of the sciences. – Robert Desgabets, Oeuvres complètes de Malebranche, 1676
Newton interjected historical remarks which were neither accurate nor fair. These historical lapses are a reminder that history requires every bit as much attention to detail as does science – and the history of science perhaps twice as much. – Carl Benjamin Boyer, The Rainbow: From Myth to Mathematics, 1957
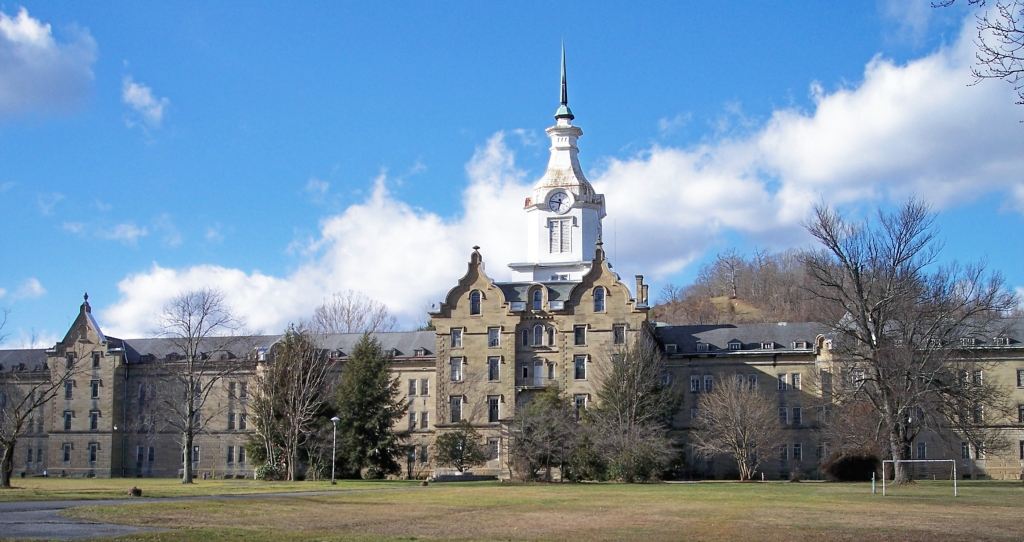


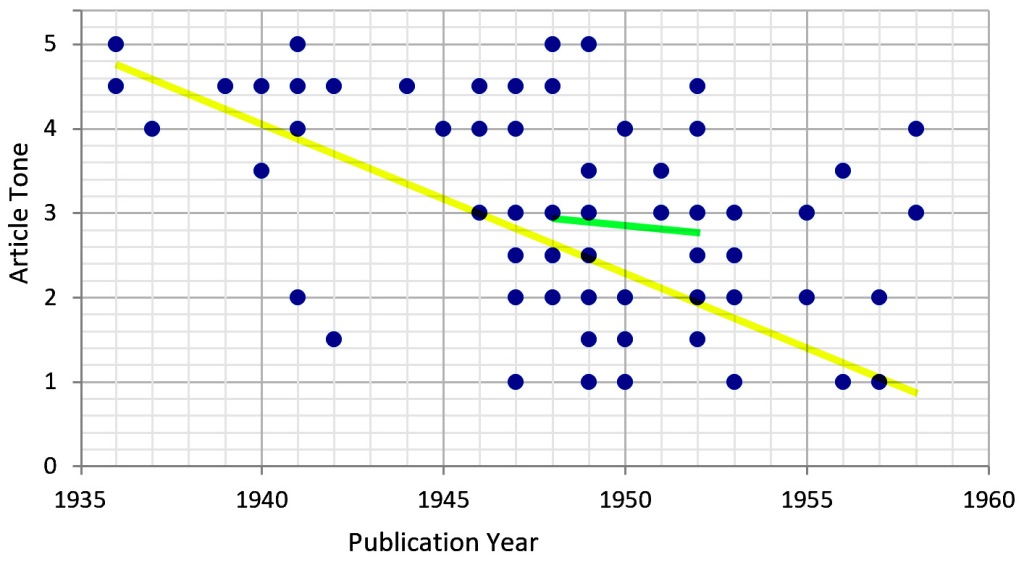
Recent Comments